Introduction
Inflation, a term widely discussed in economic circles, refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services over time. In the current economic environment, where governments worldwide have implemented expansionary monetary policies to combat the effects of the pandemic, the question arises: should investors be concerned about inflation?
In this article, we will explore the concept of inflation, its impact on the economy, investment strategies to hedge against inflation risks, and the importance of risk management and adaptability in investment decision-making.

The Impact of Inflation
To grasp the potential concerns surrounding inflation, it is important to first define inflation and understand its causes. Inflation occurs when there is an excess supply of money relative to available goods and services, leading to a decrease in the purchasing power of money. This can be caused by factors such as increased government spending, expansionary monetary policies, rising production costs, or supply chain disruptions.
The impact of inflation on the economy can be significant. As prices rise, consumers may experience a decrease in their real income, reducing their purchasing power. Businesses, on the other hand, may face higher production costs, which can lead to reduced profitability. Inflation can also erode the value of savings and fixed-income investments, as the interest earned may not keep pace with rising prices.
For example, if the price of a loaf of bread increases from $2 to $3 due to inflation, consumers will be able to buy fewer loaves of bread with the same amount of money.
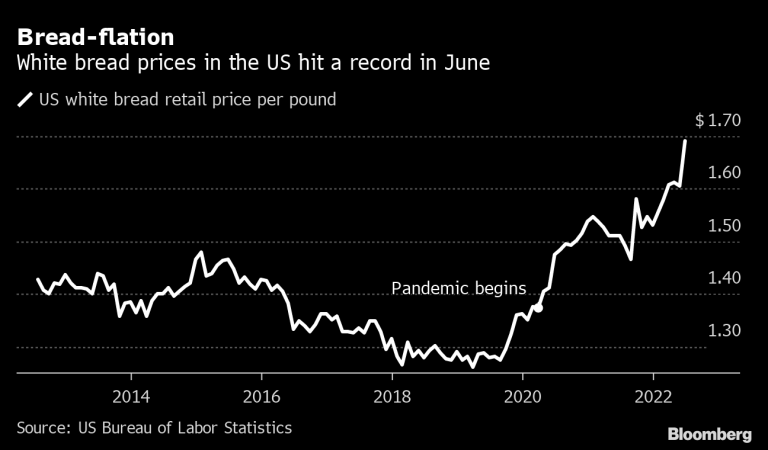
Investment Strategies to Hedge Against Inflation Risks
While inflation can pose challenges for investors, there are several strategies and tools that can help hedge against its risks:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities, can help protect against the potential negative impact of inflation on specific sectors or industries. By diversifying, investors can potentially capture the benefits of inflation-resistant assets while mitigating the risks associated with inflation-sensitive assets.
- Inflation-Protected Securities: Inflation-protected securities, such as Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS), are government bonds that adjust their principal value based on changes in inflation. These securities provide investors with a hedge against inflation, as their principal and interest payments increase with rising prices.
- Commodities and Real Estate: Investing in commodities, such as gold, oil, or agricultural products, can provide a hedge against inflation. Historically, commodities have shown a positive correlation with inflation, as their prices tend to rise during inflationary periods. Additionally, investing in real estate can also be an effective strategy, as property values and rental income often increase with inflation.
- Stocks of Inflation-Resistant Companies: Investing in stocks of companies that have a history of performing well during inflationary periods can be another strategy. These companies may include those in sectors such as utilities, consumer staples, or natural resources, which tend to have pricing power and can pass on increased costs to consumers.

Comprehensive Assessment
Inflation can have both positive and negative impacts on investors, depending on their investment strategies and risk tolerance. While inflation erodes the value of cash and fixed-income investments, it can benefit investors who hold inflation-resistant assets. Therefore, it is crucial for investors to assess their own circumstances and risk tolerance when determining whether to be concerned about inflation.
Conclusion
Inflation is a complex economic phenomenon that can impact investors in various ways. While it can erode the value of certain investments, it can also present opportunities for those who employ effective strategies to hedge against its risks.
Risk management and adaptability are key in investment decision-making, as they allow investors to navigate changing economic conditions and tailor their portfolios accordingly.
By understanding the impact of inflation, diversifying investments, and utilizing inflation-hedging tools, investors can position themselves to mitigate the potential negative effects of inflation and capitalize on investment opportunities.




